To understand better the problem that mobile device’s software have to face we need to analyze the physical medium that allows this devices to communicate, the wireless medium.
Wireless medium #
The physical layer over wireless medium has a lot of problems due to the signal nature:
- shadowing
- frequency-selective fading
- Rayleigh fading
Signal can also bounce over reflective surfaces generating reflections
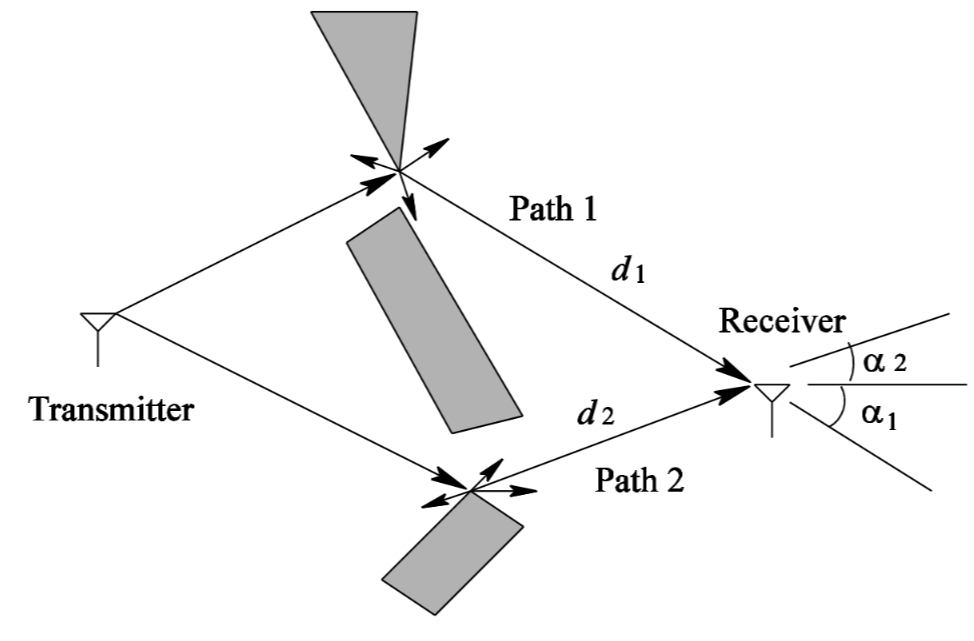
There are also meteorological conditions that can influence the signal strength.
In real scenarios with mobile nodes, mathematical models cannot be used to estimates the power loss due to the nature of the environment been to variable.
In general it can be said that power fluctuations depends on the distance from the transmitter.
ℹ️ Important
layer 2 protocols need to take into account this physical layer problems
Medium access control #
IEEE defines a section of standards for wireless connectivity technologies at data link layer under the section 802.xx
Wirelles medium access control protocols #
To manage the medium access control there are different protocols in the litterature
Csma/cd #
The CSMA/CD relies on sensing the channel and transmit only when the channel il free
In wireless environment this approach have some issues due to the nature of the nodes not being able to listen the entire channel and the node mobility
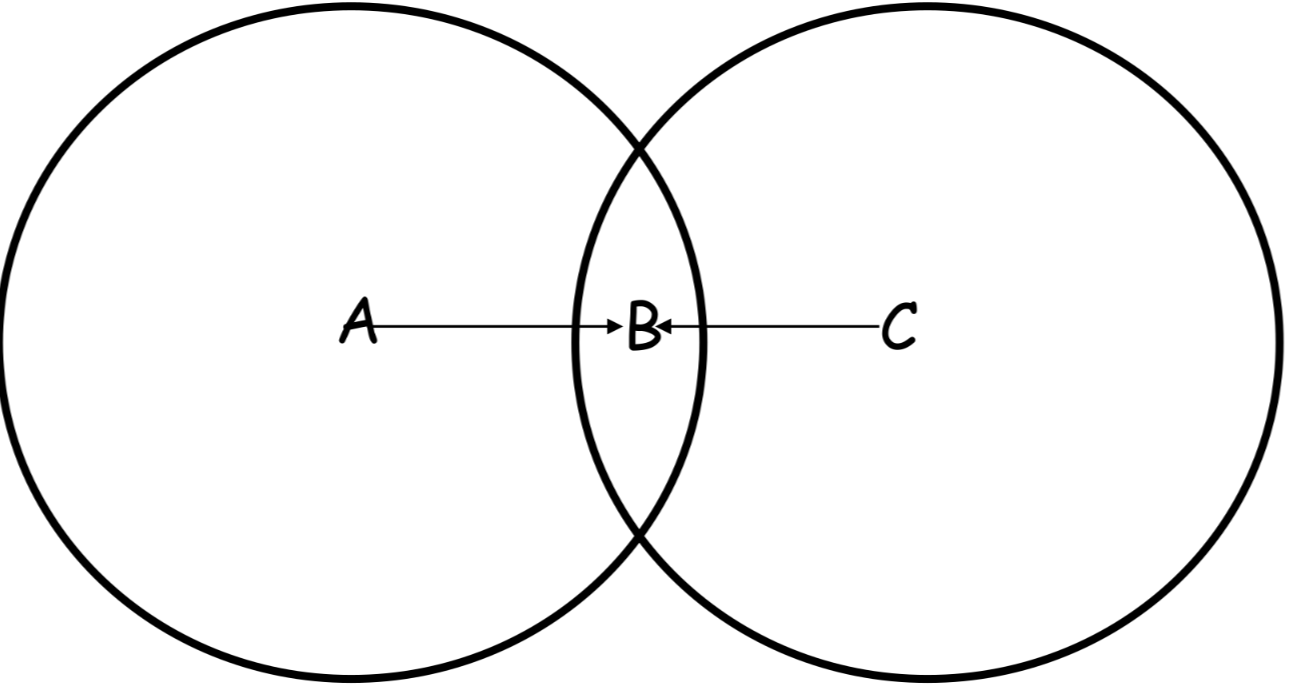
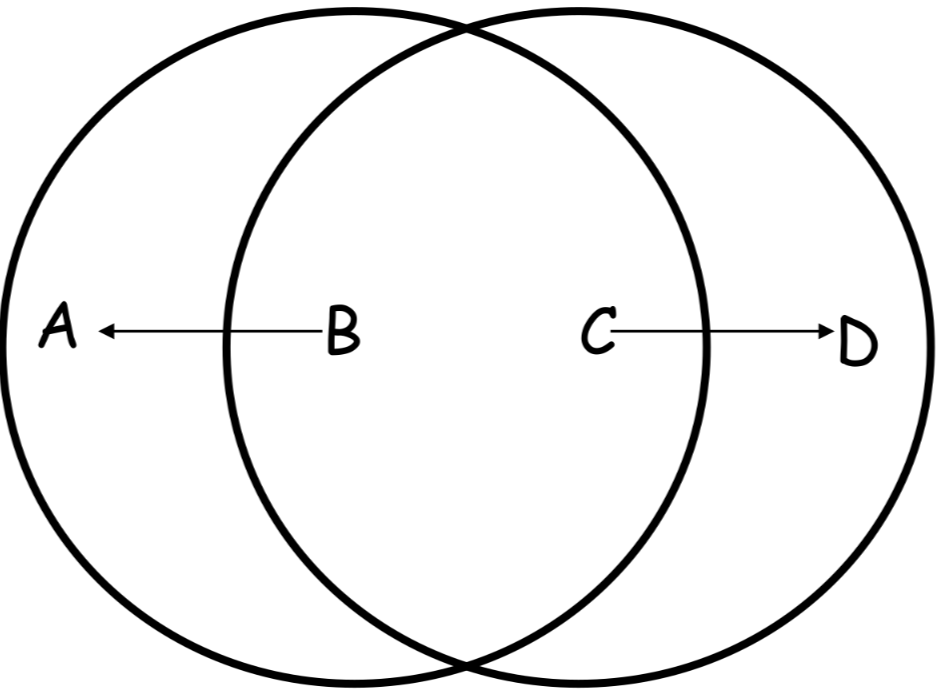
Hidden and exposed node issues #
This are particular problems that can manifest in a wireless environment where the communication is obstructed from the presence of one or more nodes in the range of the transmitter and receiver
Csma/ca variant #
A way to limit the hidden/expose node issue is to send short acknowledgment frames before transmit:
So the node A sends a request to send packet to B and wait for a clear to send reply before start transmitting the data
This solution limits collisions only to the rts and cts packets reducing the cost of re transmission but increase the overhead because every communication requires an rtc/cts exchange
Wireless architectures #
There are two possible configuration for a wireless infrastructure:
Base station mode #
The nodes are connected to a base station and communication can only append trough the base station itself
Ad hoc mode #
All nodes are potentially mobile and communicate directly